SDCCはSmall Device C Compilerの頭文字をとってこう呼ばれており、名前の通りリソースの小さなマシンで使うためのCコンパイラのことを指します。いうなれば組み込み開発で使うコンパイラのことを指します。
コマンドラインベースでコンパイルができるものになりますが、近代の開発はもはやただのコンパイラだけではなく、IDEなどの統合開発環境があることが当然でエディタもそれなりものがあって当然の時代になりました。
調べてみると意外とSDCCをスムーズに使えるようになるまでの手順があまりウェブに書かれていない気がしたので、自分で試行錯誤しながら開発環境を作ってみようと思った話です。というか自分が忘れるのでただの備忘録です。
今回私が使いたいものはPADAUKというメーカです。本来は専用の言語を使って開発するものなのですが、SDCCでコンパイルできるようにしてくれた先人がいるのでその開発環境を作ってみようと思います。おそらくこの程度だとデバッガは厳しい気がするのでコードエディタからコンパイルができるような環境を作るところを目標にします。
結果的にSDCC自体はWindows環境でインストールできたのですが、PADAUKのマイコンのOSSツールチェーンがうまく動かせなかったので、今回はWSLを使って落ち着きました。おそらく、普通にSDCCを使うだけならWindowsの方で大丈夫だと思いますが、特殊な環境だったせでそうなったという感じです。
WSL2を利用する
結論というか試行錯誤してよくわからないというところでWIndows環境から直接コンパイルするのは諦めました。最後に試行錯誤の結果は載せていますが、結局はうまく行きません。
というわけでWSLに逃げます。というわけでWLSをインストールします。細かい説明はほかのサイトの方が詳しいのでここでは雑に説明していきます。管理者でコマンドプロンプトを実行します。
wsl --install全て終わると再起動を促されるので再起動します。再起動が終わると再びWLSのインストール作業が始まるのでしばらく放置します。終わったらWindowsのメニューを開きます。するとUbuuntuが増えているのでそれを起動。するとユーザーの作成が出てくるので指示に従って作成します。
ここからはごく普通のLinux環境の作成になります。まずはaptを更新してアップデートします。
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgradeこのインストールされたUbuntuは最小の構成のようなのでgccとかも入っていないようなので色々入れておきます。
sudo apt-get install build-essential git gzip2 bison gputils flex texinfo libboost-all-dev gpasmビルド環境を整えたら次はSDCCをビルドしていきます。まずはSDCCの公式サイトにアクセスしてsnapshotから最新のソースコードを拾ってきます。そしたら以下のコマンドで解凍します。
tar xvjf xxxx.tar.bz2解凍したらビルドフォルダに移動してビルドに移ります。
cd sdcc
./configureconfigureの段階で何か足りないと出たらパッケージが不足しているので必要であれば追加します。
これが終わったら長いビルドタイムです。コンパイラのビルドは基本的に時間がかかるものなので気長に待ちます。j12としているのは自分のPCの都合なので、nprocで全力でビルドするなり好きにしてください。
make -j12全てビルドが終わったらインストールします。
$sudo make install
$sdcc -v
SDCC : mcs51/z80/z180/r2k/r2ka/r3ka/sm83/tlcs90/ez80_z80/z80n/r800/ds390/pic16/pic14/TININative/ds400/hc08/s08/stm8/pdk13/pdk14/pdk15/mos6502/mos65c02/f8 TD- 4.5.2 #15366 (Linux)
published under GNU General Public License (GPL)こんな感じで表示されればsdccのインストールができています。
次に自分の場合はPADAUKのサンプルコードをビルドしてみます。
git clone https://github.com/free-pdk/free-pdk-examples.git
cd free-pdk-examples/BlinkLEDmakeして以下のように表示されたら問題なくビルドできています。
$ make
sdcc -mpdk14 -c --std-sdcc11 --opt-code-size -DPFS154 -DF_CPU=1000000 -DTARGET_VDD_MV=4000 -I. -I../include -o .build/main.rel main.c
main.c:21: warning 283: function declarator with no prototype
sdcc -mpdk14 --out-fmt-ihx -o .output/BlinkLED_PFS154.ihx .build/main.rel
makebin -p .output/BlinkLED_PFS154.ihx .output/BlinkLED_PFS154.bin
---------- Segments ----------
. .ABS. 00000000 00000000 = 0. bytes (ABS,CON)
. .ABS. 00000000 00000000 = 0. bytes (ABS,CON)
HEADER1 00000000 00000002 = 2. bytes (ABS,CON)
HEADER3 00000000 00000014 = 20. bytes (ABS,CON)
PREG2 00000000 00000002 = 2. bytes (ABS,CON)
RSEG0 00000000 00000002 = 2. bytes (ABS,CON)
SSEG 00000006 00000001 = 1. bytes (REL,CON)
HOME 00000022 00000002 = 2. bytes (REL,CON)
GSINIT 00000024 00000014 = 20. bytes (REL,CON)
GSFINAL 00000038 00000002 = 2. bytes (REL,CON)
CODE 0000003A 00000074 = 116. bytes (REL,CON)
------------------------------
Size of BlinkLED_PFS154.bin: 174 bytesビルドできることは確認できたけどファイルの実態はどこにあるのか?となりますね。コンパイルしたファイルを確認するとともにソースコードを探してコードエディタで編集ぐらいはしたいところ。wslのファイルはデフォルトだとホームディレクトリが以下のように設定されています。
\\wsl.localhost\Ubuntu\home\(ユーザー名)ここからは先ほどビルドしたファイルを探していくだけです。あとは普通にWindowsのファイルと同じように扱えるのでファイルを煮るなり焼くなり好きにできます。
Windowsで試行錯誤(失敗)
まず初めに、SDCCそのものを入れます。
-SDCC公式サイト-
https://sdcc.sourceforge.net
Releaseのページから任意のバージョンなり最新のを入れます。インストーラ形式のものが何も考えなくてよいので楽ですね。
インストーラの指示通りに入れていき、最後にPathにSDCCを追加するか尋ねられるので、追加しておきます。
その後、Windowsの環境変数にSDCCのbinのパスが追加されているかを念のため確認しておきます。また、コマンドプロンプト上でもSDCCが認識されているかを確認してみます。sdcc --helpと入れてみます。
CMD_Windows> sdcc --help
SDCC : mcs51/z80/z180/r2k/r2ka/r3ka/sm83/tlcs90/ez80_z80/z80n/r800/ds390/pic16/pic14/TININative/ds400/hc08/s08/stm8/pdk13/pdk14/pdk15/mos6502/mos65c02/f8 TD- 4.5.2 #15366 (MINGW64)
published under GNU General Public License (GPL)
Usage : sdcc [options] filename
Options :-
General options:
--help Display this help
-v --version Display sdcc's version
--verbose Trace calls to the preprocessor, assembler, and linker
-V Execute verbosely. Show sub commands as they are run
-d Output list of macro definitions in effect. Use with -E
-D Define macro as in -Dmacro
-I Add to the include (*.h) path, as in -Ipath
-A
-U Undefine macro as in -Umacro
-M Preprocessor option
-W Pass through options to the pre-processor (p), assembler (a) or linker (l)
--include Pre-include a file during pre-processing
-E --preprocessonly Preprocess only, do not compile
--syntax-only Parse and verify syntax only, do not compile
-S Compile only; do not assemble or link
-c --compile-only Compile and assemble, but do not link
--c1mode Act in c1 mode. The standard input is preprocessed code, the output is assembly code.
-o Place the output into the given path resp. file
-x Optional file type override (c, c-header or none), valid until the next -x
--print-search-dirs display the directories in the compiler's search path
--vc messages are compatible with Micro$oft visual studio
--use-stdout send errors to stdout instead of stderr
--nostdlib Do not include the standard library directory in the search path
--nostdinc Do not include the standard include directory in the search path
--less-pedantic Disable some of the more pedantic warnings
--disable-warning <nnnn> Disable specific warning
--Werror Treat the warnings as errors
--debug Enable debugging symbol output
--cyclomatic Display complexity of compiled functions
--std Determine the language standard (c90, c99, c11, c23, c2y, sdcc89 etc.)
--fdollars-in-identifiers Permit '$' as an identifier character
--fsigned-char Make "char" signed by default
--use-non-free Search / include non-free licensed libraries and header files
Code generation options:
-m Set the port to use e.g. -mz80.
-p Select port specific processor e.g. -mpic14 -p16f84
--stack-auto Stack automatic variables
--xstack Use external stack
--int-long-reent Use reentrant calls on the int and long support functions
--float-reent Use reentrant calls on the float support functions
--xram-movc Use movc instead of movx to read xram (xdata)
--callee-saves <func[,func,...]> Cause the called function to save registers instead of the caller
--fomit-frame-pointer Leave out the frame pointer.
--all-callee-saves callee will always save registers used
--stack-probe insert call to function __stack_probe at each function prologue
--no-xinit-opt don't memcpy initialized xram from code
--no-c-code-in-asm don't include c-code as comments in the asm file
--no-peep-comments don't include peephole optimizer comments
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
Optimization options:
--opt-code-speed Optimize for code speed rather than size
--opt-code-size Optimize for code size rather than speed
--max-allocs-per-node Maximum number of register assignments considered at each node of the tree decomposition
--no-reg-params On some ports, disable passing some parameters in registers
--nostdlibcall Disable optimization of calls to standard library
--nooverlay Disable overlaying leaf function auto variables
--nogcse Disable the GCSE optimisation
--nolospre Disable lospre
--nogenconstprop Disable generalized constant propagation
--nolabelopt Disable label optimisation
--noinvariant Disable optimisation of invariants
--noinduction Disable loop variable induction
--noloopreverse Disable the loop reverse optimisation
--no-peep Disable the peephole assembly file optimisation
--peep-asm Enable peephole optimization on inline assembly
--peep-return Enable peephole optimization for return instructions
--no-peep-return Disable peephole optimization for return instructions
--peep-file <file> use this extra peephole file
--allow-unsafe-read Allow optimizations to read any memory location anytime
Internal debugging options:
--dump-ast Dump front-end AST before generating i-code
--dump-i-code Dump the i-code structure at all stages
--dump-graphs Dump graphs (control-flow, conflict, etc)
--i-code-in-asm Include i-code as comments in the asm file
--fverbose-asm Include code generator comments in the asm output
Linker options:
-l Include the given library in the link
-L Add the next field to the library search path
--lib-path <path> use this path to search for libraries
--out-fmt-ihx Output in Intel hex format
--out-fmt-s19 Output in S19 hex format
--xram-loc <nnnn> External Ram start location
--xram-size <nnnn> External Ram size
--iram-size <nnnn> Internal Ram size
--xstack-loc <nnnn> External Stack start location
--code-loc <nnnn> Code Segment Location
--code-size <nnnn> Code Segment size
--stack-loc <nnnn> Stack pointer initial value
--data-loc <nnnn> Direct data start location
--idata-loc
--no-optsdcc-in-asm Do not emit .optsdcc in asm
Special options for the mcs51 port:
--model-small internal data space is used (default)
--model-medium external paged data space is used
--model-large external data space is used
--model-huge functions are banked, data in external space
--stack-size Tells the linker to allocate this space for stack
--acall-ajmp Use acall/ajmp instead of lcall/ljmp
--no-ret-without-call Do not use ret independent of acall/lcall
Special options for the z80 port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
--allow-undocumented-instructions Allow use of undocumented instructions
Special options for the z180 port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the r2k port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the r2ka port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the r3ka port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the sm83 port:
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the tlcs90 port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the ez80_z80 port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the z80n port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the r800 port:
--callee-saves-bc Force a called function to always save BC
--portmode= Determine PORT I/O mode (z80/z180)
-bo <num> use code bank <num>
-ba <num> use data bank <num>
--asm= Define assembler name (rgbds/asxxxx/isas/z80asm/gas)
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--dataseg <name> use this name for the data segment
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
--reserve-regs-iy Do not use IY (incompatible with --fomit-frame-pointer)
--fno-omit-frame-pointer Do not omit frame pointer
--emit-externs Emit externs list in generated asm
--legacy-banking Use legacy method to call banked functions
--nmos-z80 Generate workaround for NMOS Z80 when saving IFF2
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the ds390 port:
--model-flat24 use the flat24 model for the ds390 (default)
--stack-8bit use the 8bit stack for the ds390 (not supported yet)
--stack-size Tells the linker to allocate this space for stack
--stack-10bit use the 10bit stack for ds390 (default)
--use-accelerator generate code for ds390 arithmetic accelerator
--protect-sp-update will disable interrupts during ESP:SP updates
--parms-in-bank1 use Bank1 for parameter passing
Special options for the pic16 port:
--pstack-model= use stack model 'small' (default) or 'large'
-y --extended enable Extended Instruction Set/Literal Offset Addressing mode
--pno-banksel do not generate BANKSEL assembler directives
--obanksel= set banksel optimization level (default=0 no)
--denable-peeps explicit enable of peepholes
--no-optimize-goto do NOT use (conditional) BRA instead of GOTO
--optimize-cmp try to optimize some compares
--optimize-df thoroughly analyze data flow (memory and time intensive!)
--asm= Use alternative assembler
--mplab-comp enable compatibility mode for MPLAB utilities (MPASM/MPLINK)
--link= Use alternative linker
--preplace-udata-with= Place udata variables at another section: udata_acs, udata_ovr, udata_shr
--ivt-loc= Set address of interrupt vector table.
--nodefaultlibs do not link default libraries when linking
--use-crt= use <crt-o> run-time initialization module
--no-crt do not link any default run-time initialization module
--debug-xtra show more debug info in assembly output
--debug-ralloc dump register allocator debug file *.d
--pcode-verbose dump pcode related info
--calltree dump call tree in .calltree file
--gstack trace stack pointer push/pop to overflow
--no-warn-non-free suppress warning on absent --use-non-free option
Special options for the pic14 port:
--debug-xtra show more debug info in assembly output
--no-pcode-opt disable (slightly faulty) optimization on pCode
--stack-size sets the size if the argument passing stack (default: 16, minimum: 4)
--no-extended-instructions forbid use of the extended instruction set (e.g., ADDFSR)
--no-warn-non-free suppress warning on absent --use-non-free option
Special options for the TININative port:
--model-flat24 use the flat24 model for the ds390 (default)
--stack-8bit use the 8bit stack for the ds390 (not supported yet)
--stack-size Tells the linker to allocate this space for stack
--stack-10bit use the 10bit stack for ds390 (default)
--use-accelerator generate code for ds390 arithmetic accelerator
--protect-sp-update will disable interrupts during ESP:SP updates
--parms-in-bank1 use Bank1 for parameter passing
--tini-libid <nnnn> LibraryID used in -mTININative
Special options for the ds400 port:
--model-flat24 use the flat24 model for the ds400 (default)
--stack-8bit use the 8bit stack for the ds400 (not supported yet)
--stack-size Tells the linker to allocate this space for stack
--stack-10bit use the 10bit stack for ds400 (default)
--use-accelerator generate code for ds400 arithmetic accelerator
--protect-sp-update will disable interrupts during ESP:SP updates
--parms-in-bank1 use Bank1 for parameter passing
Special options for the hc08 port:
--model-small 8-bit address space for data
--model-large 16-bit address space for data (default)
--out-fmt-elf Output executable in ELF format
Special options for the s08 port:
--model-small 8-bit address space for data
--model-large 16-bit address space for data (default)
--out-fmt-elf Output executable in ELF format
Special options for the stm8 port:
--model-medium 16-bit address space for both data and code (default)
--model-large 16-bit address space for data, 24-bit for code
--codeseg <name> use this name for the code segment
--constseg <name> use this name for the const segment
--out-fmt-elf Output executable in ELF format
--sdcccall Set ABI version for default calling convention
Special options for the mos6502 port:
--model-small 8-bit address space for data
--model-large 16-bit address space for data (default)
--no-zp-spill place register spills in 16-bit address space
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
Special options for the mos65c02 port:
--model-small 8-bit address space for data
--model-large 16-bit address space for data (default)
--no-zp-spill place register spills in 16-bit address space
--no-std-crt0 Do not link default crt0.rel
Special options for the f8 port:このように色々ヘルプが表示されれば問題なくパスが通りコンパイルできる環境が整っていることになります。
次はコードエディタ側でSDCCを使えるようにしましょう。
今回はVisualStudioCode上で開発を想定してこの上でコンパイルできる環境を考えてみます。
まずは何かしらコンパイルできるソースコードを用意します。SDCCを使う環境の場合、ご丁寧にinitしたらひな形のファイル構成を作ってくれる場合の方が稀なはずなので、ひとまずサンプルコードのようなものを用意してそこから開発を始めるのが一番手っ取り早いです。
というわけで私の場合はPADAUKのFree PDKのサイトを探して使えそうなサンプルコードを探してきました。ひとまずこれをVisual Studio Codeのファイルの部分で開きます。
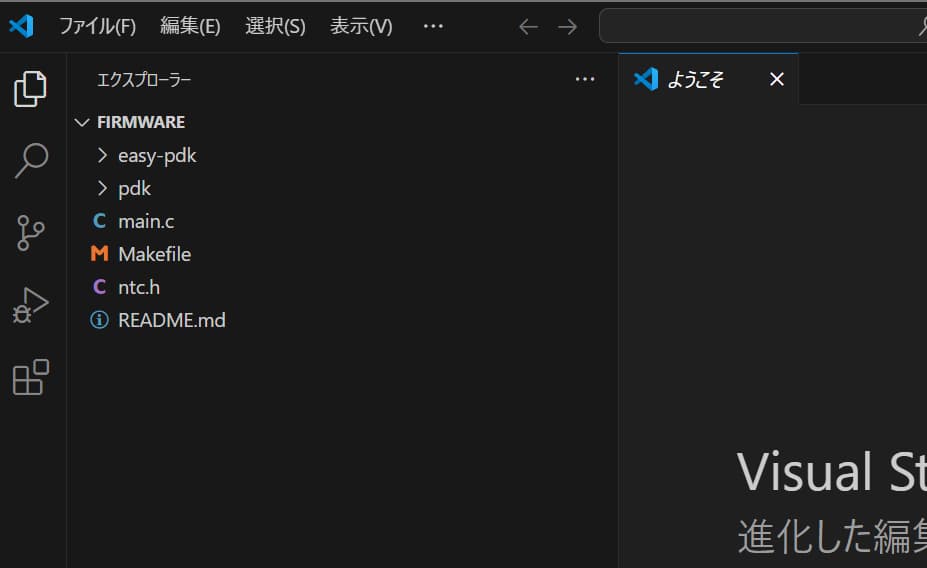
次にコンパイラの設定をします。上の画像だとタブの表示の横にある「…」を押してターミナル→タスクの構成→テンプレートからtasks.jsonを生成が検索欄に表示されるので、そこからさらにほかのコマンドを実行する例を選びます。
するとtasks.jsonが生成されるので、それをSDCCを使うように編集します。こちらのサイトに例が載っていたのでそれを拝借します。
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "sdcc",
"type": "shell",
"command": "_sdcc",
"args": [
"main"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
}
}
]
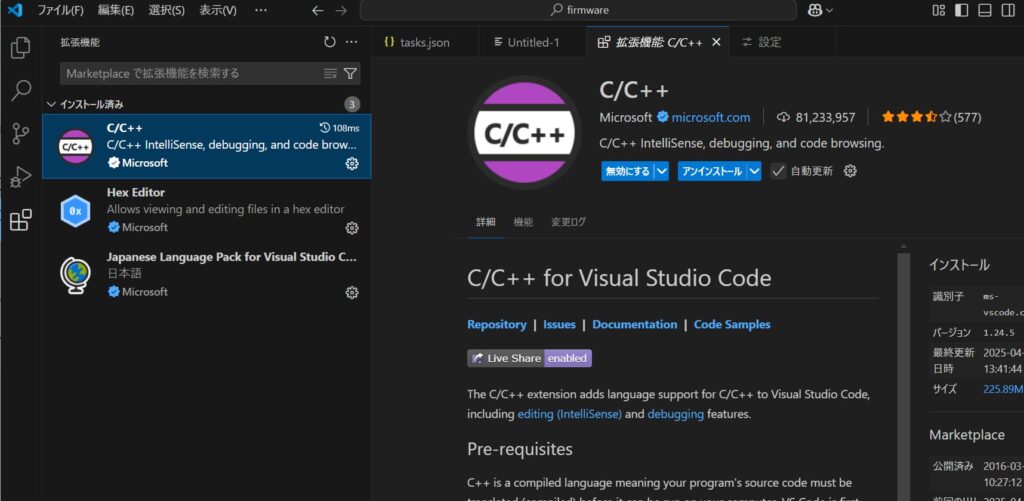
}次に以下の「C/C++」の拡張機能を入れます。発行元はMicrosoftなので安心安全。
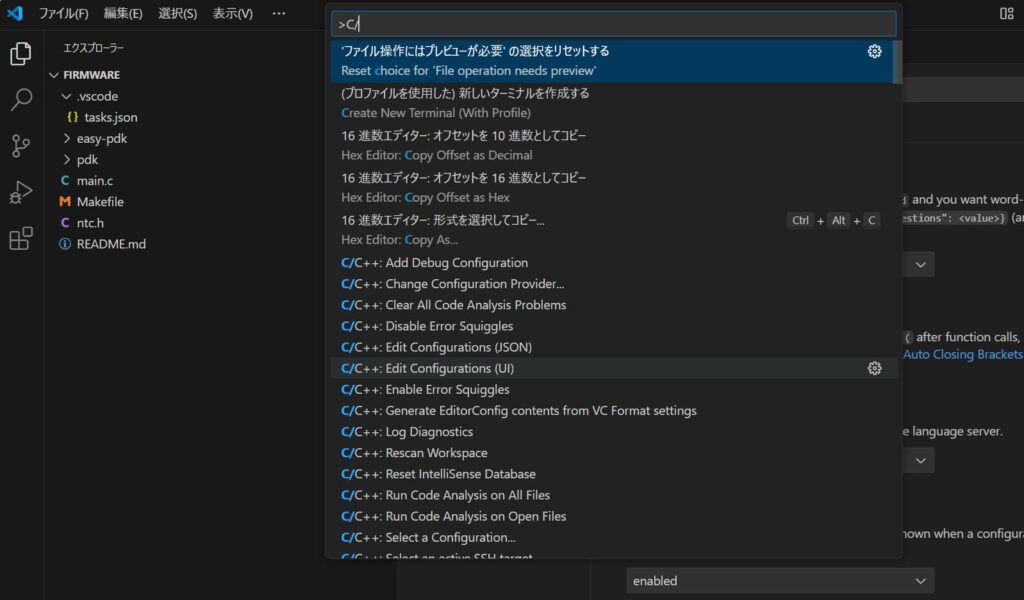
次は左下の歯車マークからコマンドトレッド→C/C++を検索してEdit Configurations (UI)を選びます。
すると色々設定項目が出てくるので構成名を適当に決めます。
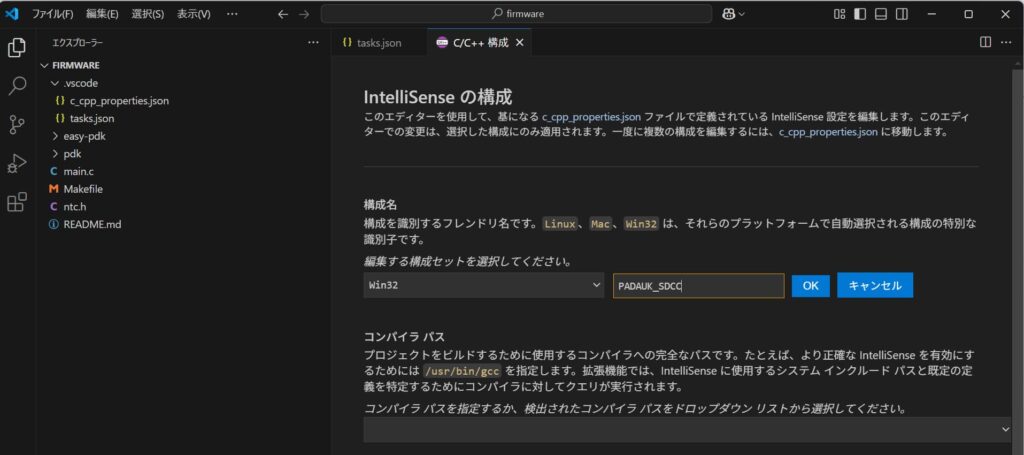
コンパイラパスには先ほど環境変数で設定された場所に入っているsdcc.exeをフルパスで指定しておきます。これで1から書いていったときのコンパイル環境ができました。
Makefileがある場合
ここまでやっておいて気づいたのですが、Makefileがある場合はmakeするだけでよいのでVSCode上でmakeしてみます。実際、私が今回サンプルに用意したプロジェクトにはMakefileが含まれていました。
ただ、Windows環境でmakeする場合はまた別に設定をしたり先ほど作成したtasks.jsonを丸々変更する必要があります。
まず初めにMake for Windowsをインストールします。サイトの下の方からインストーラをダウンロードしてひたすら次へを押していれば終わります。
しかし、実はこのインストーラは環境変数が設定されないので、環境変数としてmakeを設定する必要があります。デフォルト設定は以下のようになっているのでこれを環境変数のPathに追加します。
C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\bin追加したらコマンドプロンプトを開いて以下のようにコマンドをたたいてみます。
make -v
GNU Make 3.81
Copyright (C) 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
これはフリーソフトウェアです. 利用許諾についてはソースを
ご覧ください.
商業性や特定の目的への適合性の如何に関わらず, 無保証です.
This program built for i386-pc-mingw32こんな感じに出ればパスも正しく通っています。
ひとまずパスを通したのでTerminal上でmakeをしてみても構文エラーが表示されてうまく行きませんでした。どう考えてもWindowsでMakefileを解釈する際の影響なのですが、これをいちいち直すのも面倒ということで結局冒頭のWSLに逃げた方が早いということで逃げたという顛末です。
まとめ
やはりSDCCにせよ組み込み開発はシンプルにLinuxが一番楽だと思いました。環境が代わりにくいという点は素晴らしいです。Windowsできたらもちろん手軽で楽なのですが、Windowsアップデートしたら動かないみたいな面倒がないのが良い点です。やはり開発環境は隔離しておくに限りますね。
何はともあれWindowsではビルドできませんでしたが、Linuxならスムーズにできた点、最近はWSLのおかげで簡単にLinuxをインストールできるようになったのでその恩恵を授かることができます。本当は若干WLSに抵抗はあったんのですが、Windows上で環境を隔離しておけるのは楽だと思いました。
以上です。お読みいただきありがとうございました。